In Rastelli Raccordi they have always paid utmost attention to the environmental sustainability of their products and of machining cycles. We can then understand each aspect of the development and implementation of the finished product, from machining to packaging, obviously passing through surface treatments, which are perhaps the most delicate aspect. This commitment has allowed the company to obtain the longed-for UNI EN ISO 14001:2015 certification.
A new Zi-Ni TOTAL SCREEN treatment
Concerning in particular its zinc plating treatment, its team of engineers, in collaboration with the experts of the research and development department and of zinc plating treatment plants, has developed the new Zi-Ni TOTAL SCREEN (RRTS) system. This new treatment has been tested for all products by Rastelli Raccordi, from DIN2353-24 compression fittings to SAE J 514 – 37° adaptors as well as for hose couplings and for the whole range of BSP – BSPT – NPT adaptors.
A new hexavalent chrome- and cobalt-free electrolytic technology
The new Zi-Ni TOTAL SCREEN (RRTS) patent-pending system is based on a new hexavalent chrome-and cobalt-free electrolytic technology, so complying with the European UE2000/53/CE/RoHS standards dated 2007, implemented on the galvanic plants equipping the headquarters of Rastelli Raccordi at Villanterio (Pavia, Italy), state-of-the-art plants at zero environmental impact, where they have succeeded in obtaining a combination of exceptional protection property against corrosion, which is one of the major problems of additional costs caused by maintenances, in addition to the replacements of damaged components including downtimes and reset times. The expansion rapidity of corrosion, in fact, compels to the constant control of the aesthetical and functional condition, especially if in presence of chemical substances, saline substances, fertilizers and humid environments with high temperatures or simply exposed to air and atmospheric agents.
The surprising result of the TOTAL SCREEN (RRTS) system, which is included in the REACH regulation, has consolidated with a great distribution capability of the neatly improved and homogeneous Nickel protective layer (12-15%), achieved within a broad spectrum of current density, so granting result stability in time.

Electroplating at each point of the fitting
They have ascertained that the high penetration capacity of the bath assures the electroplating at each point of the fitting in internal areas, too. The final result is a bigger thickness in the areas that have always been more critical, that is to say in zones with low current density. The successive phases of the treatment consist in passivation and sealing, which have allowed reaching much higher technical and red corrosion resistance performances than normal standards.
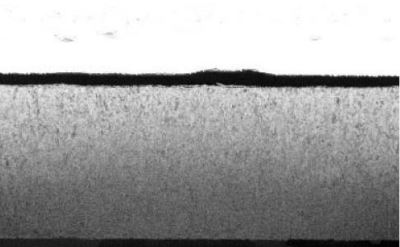
Excellent test results
To assess the validity of the zinc-plating processes adopted, products have been subjected to some tests in saline mist, tests that, with saline solution and temperature predefined by reference regulations, in short times allow simulating the exposure to aggressive agents that cause the red oxidation of the metal. Therefore, these tests permit to ascertain definitively how the protective coating behaves when exposed to the aggression in time. The tests carried out have scored really surprising outcomes, offering a much more performing protection than other systems at disposal on the market. The tests to the red oxidation have been the following in numerical terms:
- UNI ISO 9227 – 3,000 hours;
- SAE J 2334 – 60 cycles;
- ISO 16701 – 12 weeks.





